What are EMFs? What should we know about EMF radiation types? Electric and magnetic fields (EMFs) are invisible energy fields, often called radiation. The exposure generated by electrical power, charging devices, wireless signals, and both natural and artificial sources.
While low-level exposure is generally considered safe, there is growing public concern about the potential long-term effects.
This article explores common Homeowners’ questions and concerns about Electromagnetic fields.
What is EMF? (electromagnetic field)
EMF stands for Electromagnetic field, electromagnetic field or EMF radiation is a physical field produced by electrically charged objects. EMFs are present both naturally (e.g., the Earth’s magnetic field) and artificially (e.g., from electronic devices and power lines). It consists of two components, electric field and magnetic field :
Electric Field (EF)
What is Electric Field? electric field is produced by voltage, which pushes electrons through the wire. is a force field created by electric charges, influencing other charges within its range, and is measured in volts per meter (V/m).
Magnetic Fields (EMF):
What is a Magnetic Field? The magnetic field arises from the flow of current and increases in strength as the current increases, by moving electric charges (currents) and affects other moving charges or magnetic materials, measured in micro teslas (µT).
Electric fields and magnetic fields
Electric fields and magnetic fields are forms of energy, also known as Non-ionizing radiation, generated by the movement of electrons or current through wires.
Radio frequency (RF)
Radio frequency, also known as RF radiation, is a measurement representing the oscillation rate of electromagnetic radiation spectrum, or electromagnetic radio waves, from frequencies from 300 gigahertz (GHZ) to as low as 9 kilohertz (kHz)
Dirty electricity (DE)
What is dirty electricity? Dirty electricity is erratic frequencies riding on our electrical wires, making the EF frequency even more disturbing to our bodies, caused by various electronics and the household devices
Electromagnetic Spectrum
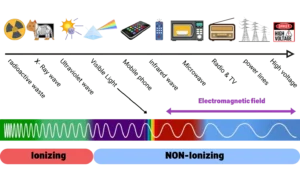
Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) cover a wide spectrum of frequencies, from extremely low frequencies (ELF) to high-frequency radiation like X-rays and gamma rays. Here’s a breakdown of the full EMF spectrum:
- Radio Waves EMF frequencies used in broadcasting and communications.
- Microwaves EMF: Found in microwave ovens and mobile networks.
- Infrared Radiation EMF: Used in remote controls and heat detection.
- Visible Light EMF: The only part of the spectrum visible to the human eye.
- (UV) Ultraviolet Radiation EMF: Emitted by the sun, responsible for sunburns.
- X-Rays EMF: Used in medical imaging.
- Gamma Rays EMF fields: High-energy radiation often produced by nuclear reactions.
electromagnetic radiation (EMR)
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) is a form of energy that travels through space as waves made up of both electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicular to each other. This energy moves at the speed of light (c = 299,792,458 m/s) and does not require a medium to propagate.
Types of EMF Frequency and Sources
Electric and magnetic forces in EMF fields result from electromagnetic radiation. EMFs fall into two categories: ionizing radiation, which can directly damage DNA and cells and non-ionizing radiation.
- Ionizing Radiation: High-frequency radiation, such as X-rays and gamma rays, which has enough energy to ionize atoms and potentially cause cellular damage.
- Non-Ionizing Radiation: Lower frequency radiation, such as radio waves and microwaves, which is generally considered less harmful but still under scientific investigation for long-term effects.
| Type of Radiation | Frequency Range | Wavelength Range | Common Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radio Waves | 3 kHz – 300 GHz | >1 mm | AM/FM radio, TV, Wi-Fi, Cell Phones |
| Microwaves | 300 MHz – 300 GHz | 1 mm – 1 m | Microwave ovens, 5G, Radar, Satellites |
| Infrared (IR) | 300 GHz – 430 THz | 700 nm – 1 mm | Heat lamps, Remote controls, Thermal cameras |
| Visible Light | 430 THz – 770 THz | 400 nm – 700 nm | Sunlight, LED bulbs, Lasers |
| Ultraviolet (UV) | 770 THz – 30 PHz | 10 nm – 400 nm | Sun, Tanning beds, Black lights |
| X-rays | 30 PHz – 30 EHz | 0.01 nm – 10 nm | Medical imaging, Airport security scanners |
| Gamma Rays | >30 EHz | <0.01 nm | Nuclear reactions, Cosmic rays, Radioactive decay |
Key Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation:
- Wave-Particle Duality: EMR behaves both as a wave and as a particle (photon).
- Travels in a Vacuum: Unlike sound waves, EMR does not need air, water, or any medium.
- Carries Energy: The amount of energy depends on the frequency (higher frequency = more energy).
- Can Interact with Matter: It can be absorbed, reflected, refracted, or transmitted through different materials.
Can EMFs Be Harmful to Health?
We have a detailed blog on EMF frequency health effects and EMF toxicity symptoms based on global research. It almost began in the 1990s. Most EMF radiation research focused on extremely low-frequency exposures stemming from conventional power sources, such as power lines, electrical substations, or home appliances.
While some of these studies showed a possible link between EMF field strength and an increased risk for health, their findings indicated that such an association was possible. Some studies that have been conducted on adults show no evidence of a link between EMF exposure and adult cancers, such as leukemia, brain cancer, and breast cancer.

Safe EMF levels for humans
Safe EMF exposure levels for humans vary by frequency. The ICNIRP guidelines recommend limiting exposure to 2 mG (milligauss) for low-frequency EMFs and below 1.6 W/kg SAR (Specific Absorption Rate) for radiofrequency EMFs used in wireless devices
Well, you may ask, what emits the most EMFs at home? The highest EMF frequency sources in homes include Wi-Fi routers, microwaves, cordless phones, smart meters, and electrical wiring. Other common sources are induction cooktops, refrigerators, and baby monitors, which emit low-to-moderate EMFs
Does WiFi emit EMF?
Are EMFs from cell phones harmful?
Other Electromagnetic Examples
In the age of electronic vehicles, cellular telephones, wireless routers, and the Internet of Things, all of which use EMF, additional and practical ways to reduce exposure to EMFs at home.
Here are some common real-life examples of electromagnetic fields:
Household Electronics: TVs, computers, and refrigerators emit EMFs.
Wireless Communication: Cell phones, Wi-Fi routers, and Bluetooth devices operate on electromagnetic waves.
Power Lines: High-voltage power lines generate low-frequency EMFs.
Medical Imaging: MRI machines use strong magnetic fields for diagnostic imaging.
How do EMF Contractors reduce EMF exposure?
It is a wise decision to ask an EMF specialist to conduct a professional EMF inspection for safer environments. After they find the sources for EMF exposure and the cause of it, they usually use one of these methods.



